David Gill might be the richest man in Sebastopol, California. The semi-retired health care administrator is banking the most valuable currency in the world: time. Gill currently has 480 hours in his savings account at the local time bank, “and I haven’t even registered any of my hours in 2023,” he says.
In brief, a time bank does with time what other banks do with money: It stores and trades it. “Time banking means that for every hour you give to your community, you receive an hour credit,” explains Krista Wyatt, executive director of the DC-based nonprofit TimeBanks.Org, which helps volunteers establish local time banks all over the world. Nobody keeps track of the exact number, but thousands of time banks with several hundred thousand members have been established in at least 37 countries, including China, Malaysia, Japan, Senegal, Argentina, Brazil and in Europe, with over 3.2 million exchanges. There are probably more than 40,000 members in over 500 time banks in the US.
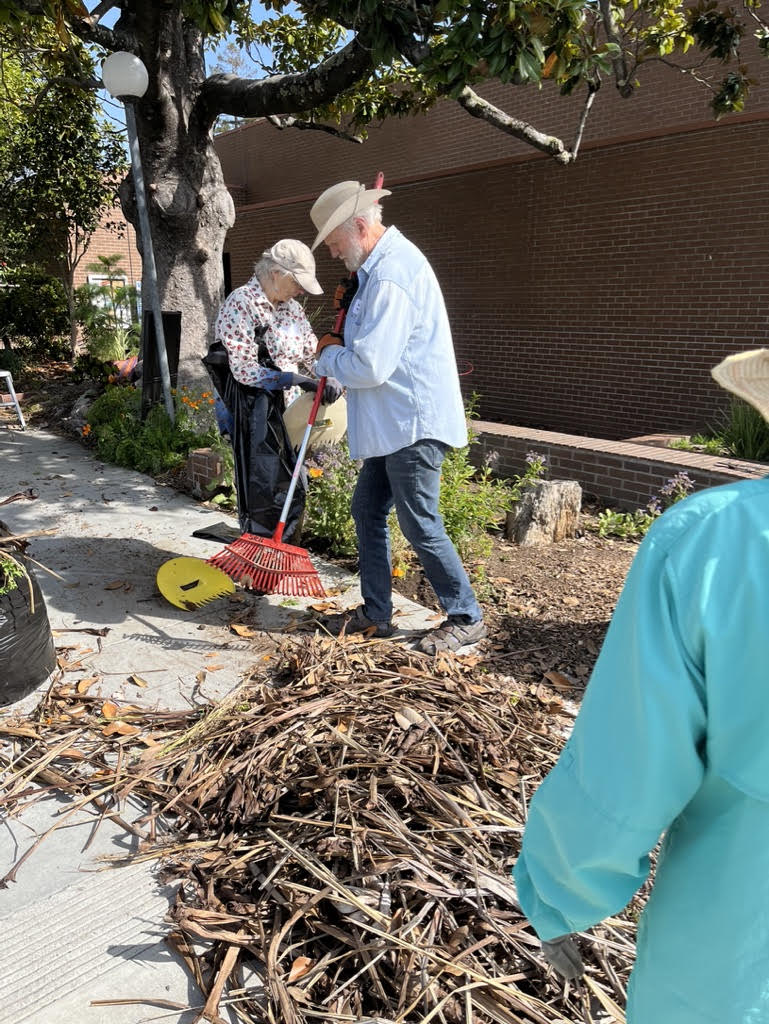

In Sebastopol, 250 residents have time bank accounts where they save and withdraw hours as needed. For instance, Gill, who is also the main local time bank coordinator, likes to offer his expertise with computer programming, editing and financial planning. In return, he asks for help when he needs a ride to the airport or someone to transport heavy furniture. He rattles off the first few of many examples: “Steve, who lives on the next block, drove me and my partner to the Santa Rosa airport. Ken fixed the icemaker in our refrigerator, and Elaine did some electrical work.”
If he had called professional repair and taxi services, the expense would have been significant. However, the interest, so to speak, goes beyond the value of a mere transaction. The time banks are building social capital. “I’ve made wonderful friends I wouldn’t have met otherwise and we now invite each other to our garden parties,” says Gill. “It’s about making community and being a part of the community. You can’t put a price on that stuff.”
David Gill came to the time bank like most of his neighbors. He doesn’t remember where he first heard about it a few years ago, but he immediately thought it was a great idea. He signed up, started using it, and when the founders asked for help, he stepped up. He gets paid in the currency he values most: hours.
Many time banks are volunteer community projects, but the one in Sebastopol is funded by the city and operates under the nonprofit status of the Community Cultural Center. After all, time is money. “Every volunteer hour is valued around $29,” Wyatt calculates. “Now think about the thousands of dollars a city saves when hundreds of citizens serve their community for free.” The Sebastopol time bank has banked more than 8,000 hours since its launch in 2016. Members might reimburse each other for costs — for instance, gas mileage or materials — but the service itself and the membership are always free.

Some cities look to time banks as a model to support an aging population. In St. Gallen, Switzerland, only members over the age of 50 may join the local Stiftung Zeitvorsorge, or “Foundation Time Care,” which was founded in 2011 and has 320 members who have banked more than 80,000 hours. While Sebastopol’s time bank is more geared toward practical services to fill a gap other community services don’t address, members in St. Gallen regularly help seniors run errands, shop for groceries, take them to the doctor or simply keep them company. Here, too, the city guarantees the program, hoping that it will help seniors to stay in their homes and live independently longer because 75 percent of locals said in a poll that they hoped to stay in their homes as long as possible. Even if only five people were enabled to enter care homes a year later, the foundation’s executive director Jürg Weibel recently told the German magazine Der Spiegel, the investment would have already recouped itself. “The reality is that grown-up kids live in other areas,” Weibel said. “Also, many seniors are consciously looking for a new purpose.”
The time banks in both Sebastopol and St. Gallen have more offerings than demand. In a way, they have too much time in the bank, not least because seniors are looking to get help later in life.
Weighed down by negative news?
Our smart, bright, weekly newsletter is the uplift you’ve been looking for.“Seniors have a lot to offer,” Gill believes. While he points to his white hair as “pretty representative of the age of our time bank members,” some universities and schools have established time banks specifically for students and teachers at their institutions.
The idea of time as a bankable currency goes back to a Japanese seamstress and activist, Teruko Mizushima, who traded her sewing skills for fresh vegetables during the Pacific War in the early 1940s. In 1973, she started the first “Volunteer Labour Bank” that soon included thousands of members.

In the US, the civil rights lawyer Edgar Cahn, who worked as a speechwriter for Robert F. Kennedy and executive assistant to Peace Corps founder Sargent Shriver, rediscovered the idea of time banks as allies to fight poverty in the early 1960s, when money for social programs had dried up. He later coined the term “Time Dollars” and trademarked “Time Bank.” In 1995, he founded the nonprofit Krista Wyatt now works for as a hub of resources, first under the name “Time Dollar Institute.” “When he was bedridden in a hospital after a severe heart attack, he felt ‘useless,’ and saw time banks as a way for everyone to contribute to the community, no matter their age or qualifications,” Wyatt explains.
Cahn formulated five core principles that guide time banks to this day: First, everyone has something to contribute. Second, valuing volunteering as “work.” Third, reciprocity or a “pay-it-forward” ethos. Fourth, community building, and fifth, mutual accountability and respect.
“What captured me is that people are doing things out of their own good heart,” Wyatt says. “Many years ago, a woman got really upset because, as she said to Edgar Cahn, ‘I have nothing to give.’ Edgar Cahn listened and finally responded, ‘You have love to give.’ And the whole room just went silent.”
Every hour of service is valued the same, no matter how much skill and expertise a task takes, whether it’s an hour keeping someone company, helping them file their taxes or repair a roof. Through a simple online platform, every member can offer and request services and then register the hours they served or received. Especially during and since the Covid pandemic, the bank has also been an antidote to the epidemic of loneliness. For instance, the Sebastopol time bank regularly hosts in-person events and meetings.
“We do events where everybody brings a list of five things they need to get done,” Wyatt gives an example. “You wouldn’t believe how many things get crossed off these lists in a room full of people who are willing to help.”
Wyatt came to TimeBanks after supporting cancer survivors. She’d read Cahn’s 2000 book, No More Throw-Away People, and was looking for a way to give back. “There are people like me who like to work on the computer rather than cleaning my garage,” Wyatt says, “and there are people who’d rather clean a garage than be stuck behind a computer. Everybody can be part of the time bank community. It’s as simple as that.”
In a way, time banks are the 2.0 version of what used to happen organically in small communities: Neighbors and colleagues would help each other out. “Now we simply do it with the help of a computer,” Gill says. “Or you may just pick up the phone and call another member directly rather than post a request online. It helps to get to know the various members.”

While the core principles are simple, both Wyatt and Gill acknowledge that implementing and managing the time bank well is a complex task. They both spent countless hours trying out different software programs before settling on a program that works well for them.
Wyatt dreams of connecting the various time banks internationally so that someone in, say, San Francisco, could learn French with a time bank member in Paris. Or a tourist traveling in Japan could meet local time bank members there and, after her return, show other tourists around her own town.
Interpreted this way, the time credit functions as an alternative currency. Members can also donate their services to community members in need and the community without banking a credit for themselves.
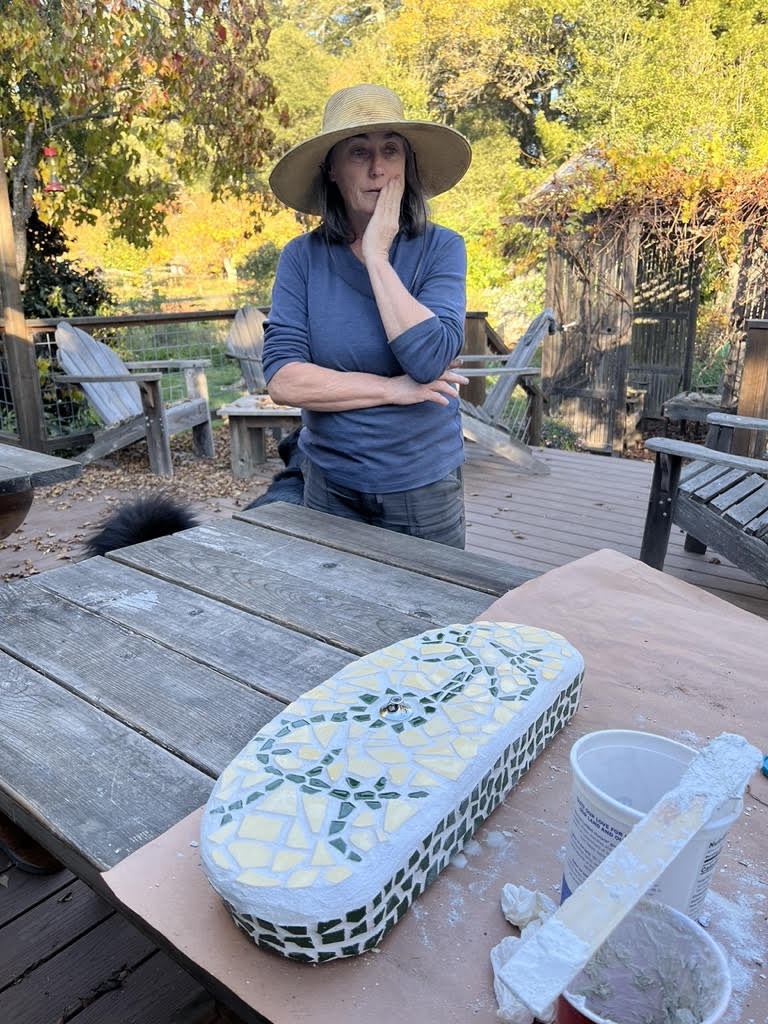
For instance, in Sebastopol, artist Ellie Kilner completed a giant sculpture at the Sebastopol Senior Arts Center and other art projects with the support of fellow time bank members.
Gill’s favorite exchange, so far, also has to do with art and with a broken toilet cover. Because the toilet was an ancient model, it was impossible to find a replacement. He posted a request for help on the time bank’s online platform, and a local mosaic artist not only glued the broken pieces together but turned it into a colorful piece of art. “Now it’s a conversation piece!” Gill raves. He says he plans to request more work from this artist, Elizabeth Newton.
He is clearly passionate about his role in facilitating the time bank and everything that time banks can provide: “I don’t think we can ever have too many friends or too much community.”












