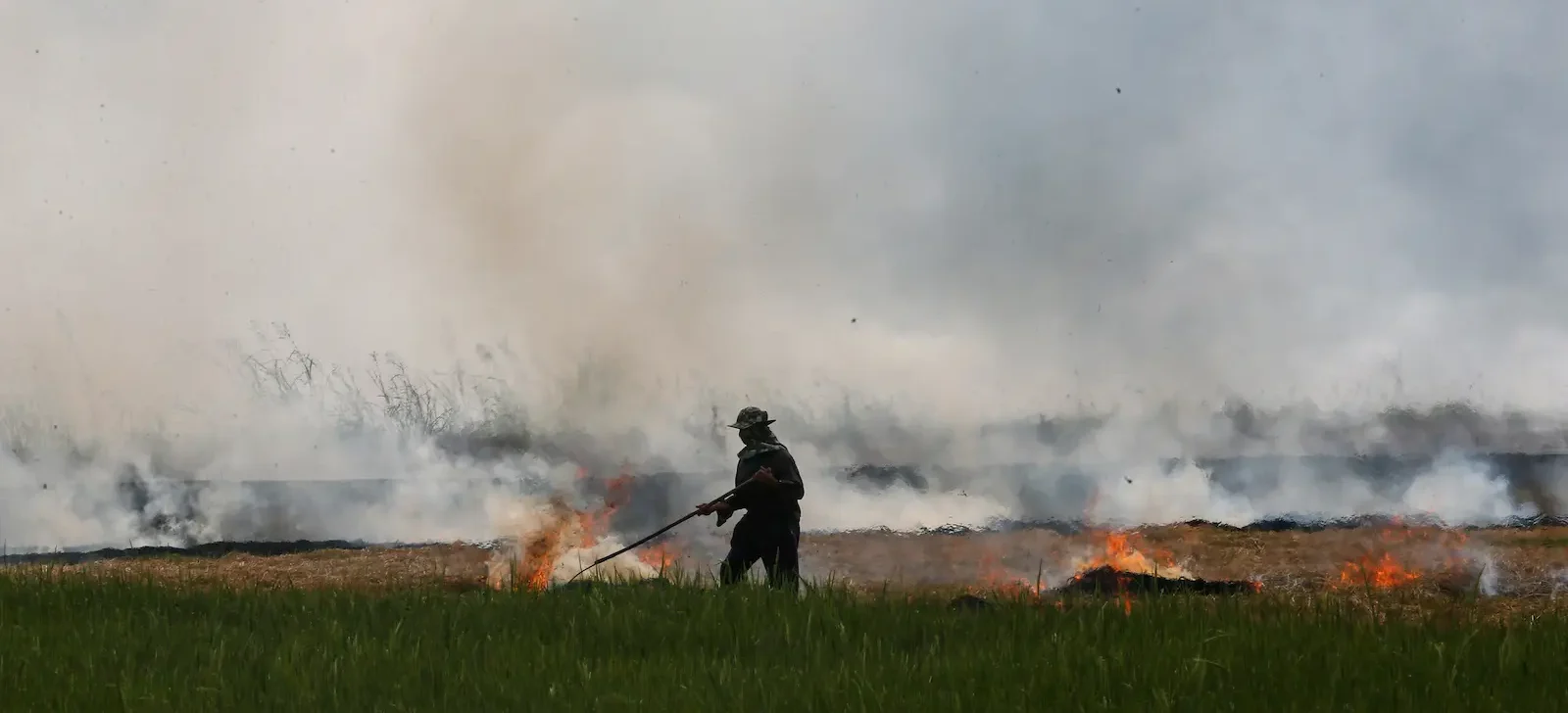
When Gufasha Moureen was 13 years old, a severe drought hit her village in the Kayunga district of Uganda. All her family’s crops were destroyed, sending them into a financial crisis.
Being the eldest daughter of five children, she had to leave school and help her mother at home with fetching water, cooking and childcare. One day, an elderly man visited their home and told Moureen’s father that he wanted to marry her.
Her father, who was in desperate need of money and saw no other option for Moureen, agreed. Moureen married, got pregnant and died the same year during a complicated childbirth.

“That is just one of many devastating stories of how climate change affects young girls worldwide. Had the drought not hit her village, Moureen could have stayed at school and her life could have been different,” says Joan Kembabazi, Moureen’s best friend and founder of Gufasha Girls Foundation, a community-based nonprofit that advocates against child marriage and promotes girls’ education.
In Uganda, young girls and women face multiple challenges. Not only are they disproportionately affected by climate change but they also have limited access to modern contraceptive methods and have no comprehensive sexual and reproductive health education at schools (it was banned by the Parliament in 2016), which makes them even more vulnerable.
Kembabazi sees family planning as an essential tool for climate resilience. That’s why she’s committed to empowering girls and women with education and contraception. “I myself come from a big family and I know how hard it is for my father to provide for his 24 kids,” says the young Ugandan feminist activist. “If he had two or three, it would be much easier.”
Gufasha Girls Foundation is one of many organizations worldwide working to address the ways that poverty, food insecurity, climate change and family planning are linked — and the need to empower girls and women through education and family planning.
Healthy communities, healthy environment
In the Philippines, the PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc. (PFPI) has pioneered an approach that addresses population, health and the environment. When it started in the 1990s as a public health organization raising awareness about the prevention of HIV and AIDS, the foundation worked with young girls who moved to cities to work in the sex industry to support their families at home.
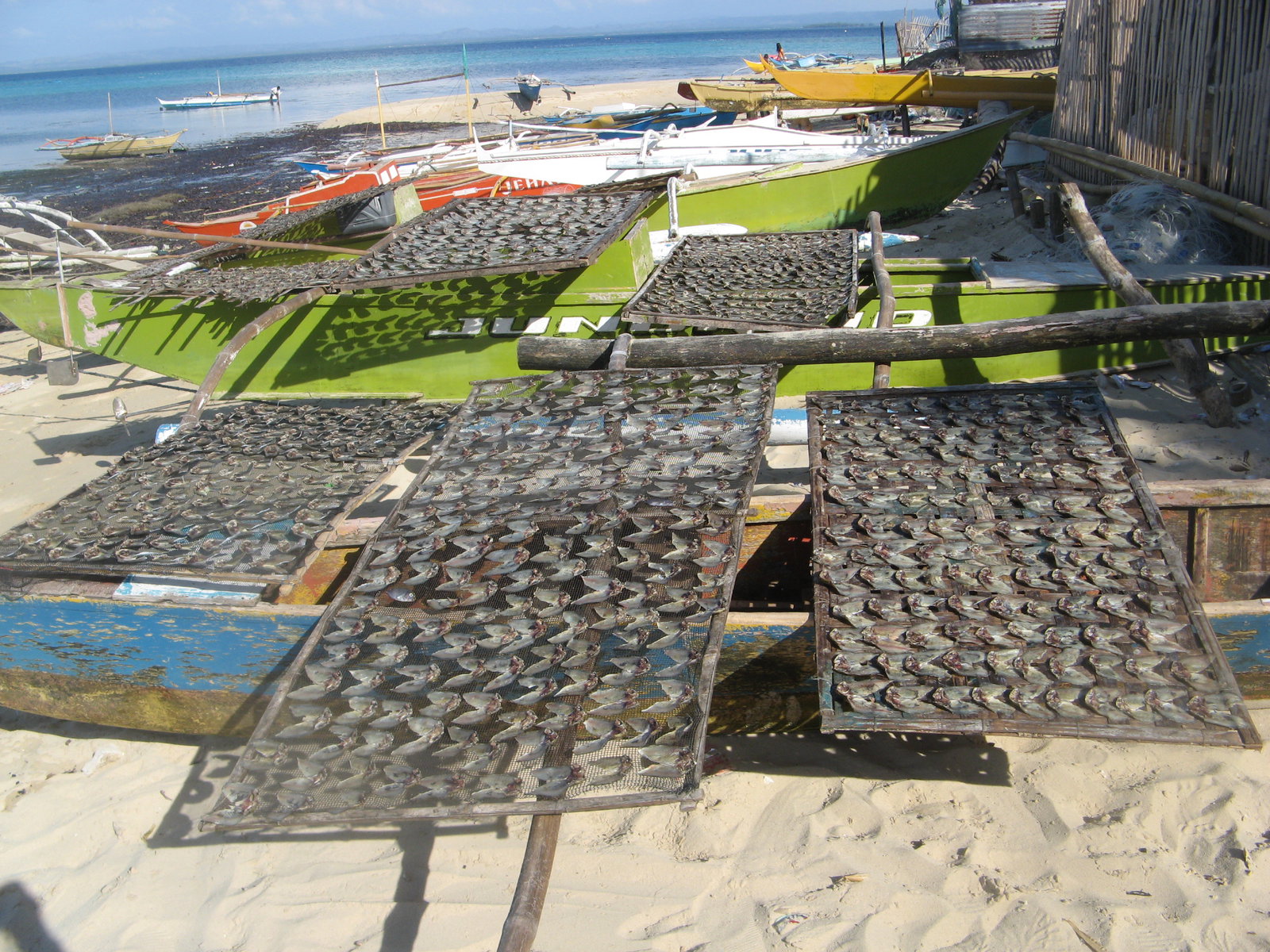

PFPI staff understood that if they wanted to help prevent young girls from contracting HIV, they would have to look at the root causes that led them to this line of work. They went to the poor fishing communities where the girls came from (namely the Danajon Bank and Verde Island Passage, which are extremely rich in marine biodiversity) and learned that fishermen there were facing pressure to catch more fish to sustain a growing population.
But since the fish stocks did not have time to regenerate, there were fewer fish every year. This meant that the families had less food and income and were more inclined to send their daughters away to contribute to the budget.
Between 2008 and 2013, PFPI worked with other organizations and the local community to improve the management of 2,000 hectares of marine protected areas. They designated areas where fishermen could fish and areas where fishing was prohibited to give the fish stocks time to regenerate.
Crushed by negative news?
Sign up for the Reasons to be Cheerful newsletter.Over the course of five years, the fish stocks increased and the food security and economic situation improved. The fishermen also started branching out into other ways to make money, such as selling produce from vegetable gardening, livestock and fowl keeping, running small businesses and tourism.
Besides sustainable management of resources, PFPI also addressed the health needs of the communities. In these isolated rural areas where access to contraceptives was limited to only a few health clinics, it partnered with small convenience stores that started selling condoms and birth control pills in every village.
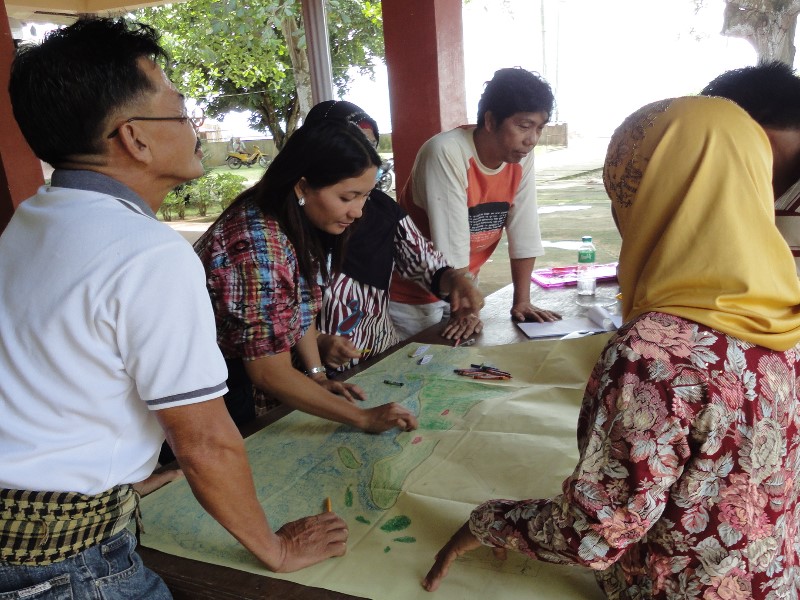

The foundation worked with local leaders — mainly youth, couples, women and fishermen — who then educated their peers about the benefits of family planning, HIV prevention, water and sanitation and malnutrition. Through these peer educators and educational shows on local TV and radio, PFPI was able to reach 1.5 million people. As a result, the rate of contraceptive use among married women of reproductive age increased from 31 percent to 45 percent.
Following its success in the Philippines, PFPI has been advocating for this integrated approach to address climate change, food insecurity and public health in other places in need around the world.
A lack of recognition
On the local level, this approach has been replicated in many parts of the world, including in Venezuela, Colombia, Madagascar, Uganda and Nepal). But on the national level, securing climate and gender justice is not always high on policy makers’ priorities.
At last year’s COP28 in Dubai, representation of women was staggeringly low: only 15 out of 133 world leaders present were women. “When it comes to decision-making power, you can’t make decisions that have the whole world in mind when half the population is not represented in the room,” says climate and community development expert Carissa Patrone Maikuri.
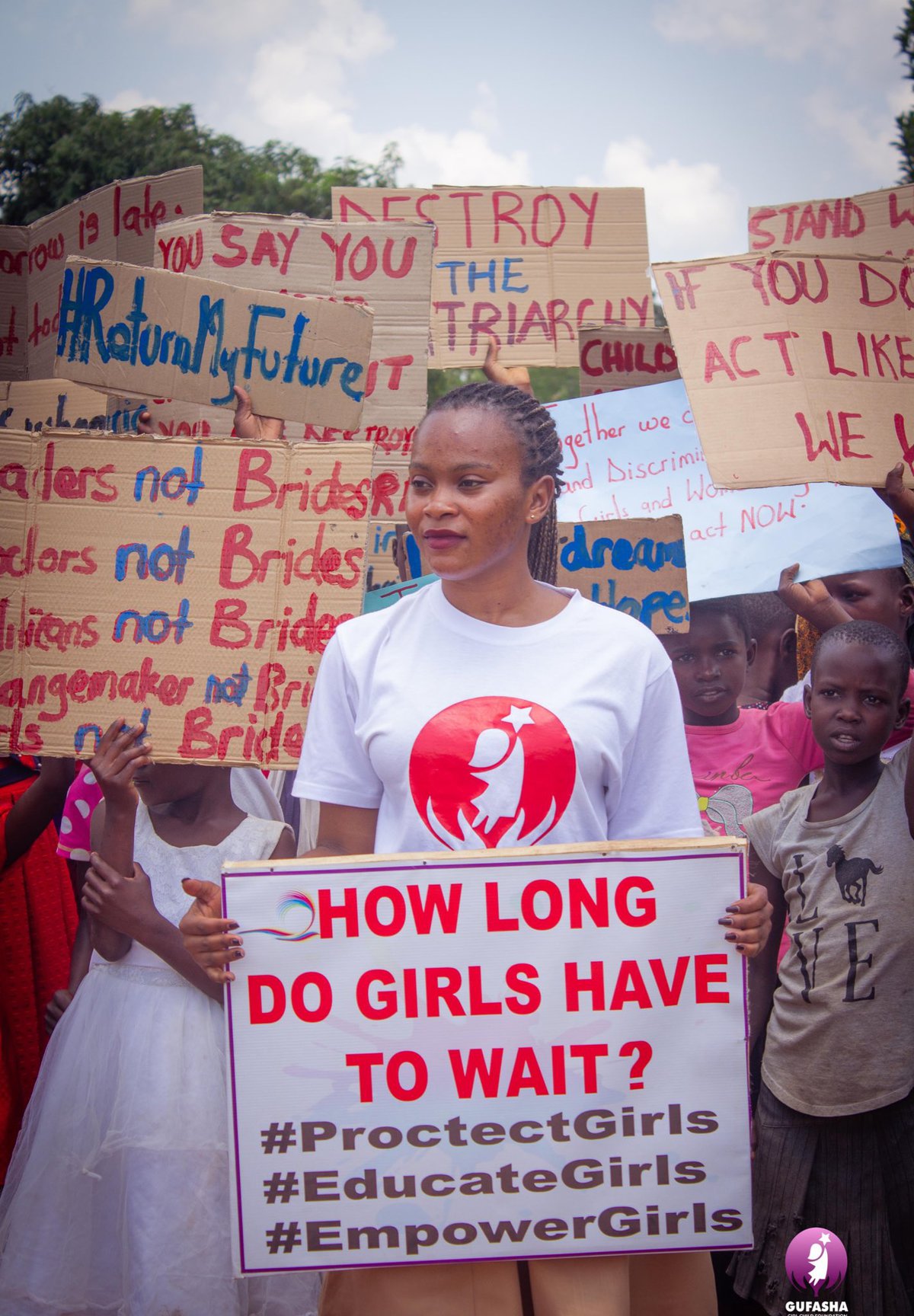
According to the Feminist Climate Justice report, by 2050, up to 158 million more girls and women might be pushed into poverty due to climate change. And yet, many countries’ adaptation plans still don’t mention sexual and reproductive health and rights or universal education as essential human rights or as important adaptation strategies.
Presently, more than 218 million women in low- and middle-income countries want to avoid pregnancy but are not using a modern method of contraception. Globally, nearly half of all pregnancies are unintended.
Turning the tide
It makes sense that, when women are able to choose whether, when, with whom, or how many children to have, they can further pursue their education, tend to have better access to work opportunities, and can improve their own health and that of their families. But the connection to climate change can be harder for people to make.
Patrone Maikuri is among those working to spread the message that family planning can boost women’s resilience to environmental and climatic shocks and stressors. “Many climate folks don’t understand how sexual and reproductive health and rights [are] connected to climate resilience, and as a result, they shy away from the conversation,” she says. “But in the past few years, there has been a small movement that is looking at climate action in a more holistic and intersectional way.”
A growing number of international organizations have been advocating for gender equality and women’s and girls’ reproductive rights to be embedded into climate solutions and climate justice. For example, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change highlighted voluntary and rights-based family planning as a climate adaptation strategy in its 2014 assessment report. And in 2023, the UN Women called for a new feminist climate justice approach.
The tide is turning, according to Carina Hirsch, head of advocacy and policy at the nonprofit Margaret Pyke Trust. She points to the growing alliance of health-focused organizations that are advocating at a national level with both climate and conservation sectors as well as growing interest from donors to fund this kind of work.

For her, one of the most exciting recent developments was the announcement at COP28 that the UK will provide £16 million in funding focused on the importance of reproductive choice as part of climate resilience building.
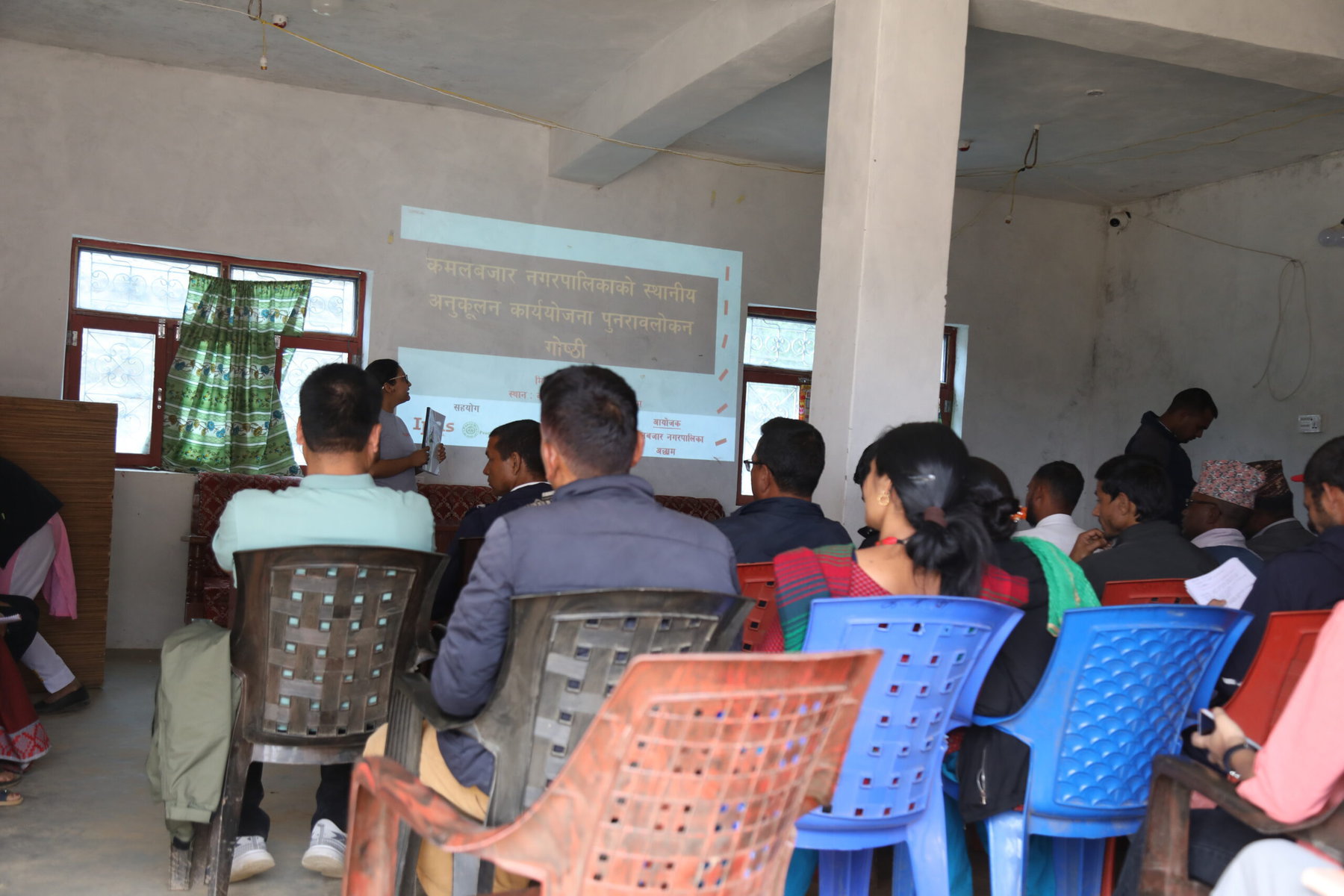
Khusbu Poudel, the program coordinator at reproductive rights nonprofit Ipas Nepal, sees this as a welcome change. Nepal is one of the most climate vulnerable countries in the world, and Ipas Nepal helped local governments prepare Local Adaptation Plans for Action, which integrate gender, climate and sexual and reproductive health and rights. “Investing in women, children and adolescents is one of the most impactful climate actions a country can make,” says Poudel, who participated at COP28.
The urgency, Hirsch notes, is clear: “We cannot wait. Climate change is coming no matter what and we know it,” she says. “The least we can do is to make people, particularly women and girls in remote rural communities, that are being hit hardest by climate change, more resilient.”









